1 核心概念和作用
定义:允许 AI 模型调用外部工具(如 API、数据库查询),扩展模型能力,实现信息检索和操作执行。
两大应用场景:
- 信息检索:获取实时数据(如天气、新闻),支持 RAG 场景。
- 操作执行:自动化任务(如发送邮件、创建数据库记录)。
安全机制:模型仅能请求工具调用,实际执行由应用负责,模型无法直接访问 API。
2 快速开始
信息检索工具(获取当前时间)
先定义一个自定义的工具类,提供获取当前时间的方法
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
| public class DateTimeTools {
@Tool(description = "获取用户时区的当前日期和时间")
String getCurrentDateTime(){
return LocalDateTime.now().atZone(LocaleContextHolder.getTimeZone().toZoneId()).toString();
}
}
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
| @Test
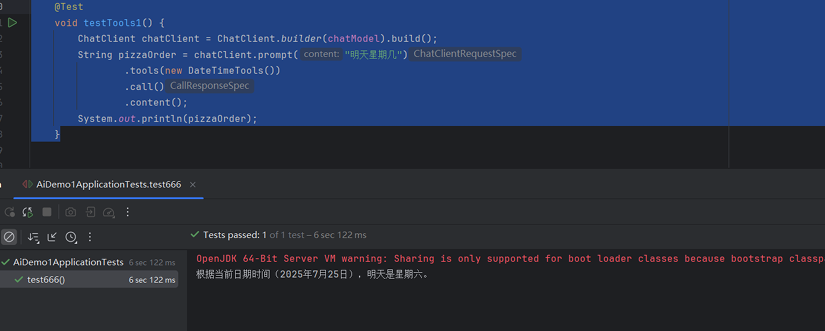
void testTools1(){
ChatClient chatClient = ChatClient.builder(chatModel).build();
String prizzaOrder = chatClient.prompt("明天星期几")
.tools(new DateTimeTools())
.call()
.content();
System.out.println(pizzaOrder);
}
|
效果
操作执行工具(设置闹钟)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
| public class DateTimeTools {
@Tool(description = "获取用户时区的当前日期和时间")
String getCurrentDateTime(){
return LocalDateTime.now().atZone(LocaleContextHolder.getTimeZone().toZoneId()).toString();
}
@Tool(description = "设置指定时间的闹钟,时间格式为 ISO-8601")
void setAlarm(@ToolParam(description = "ISO-8601 格式时间") String time) {
LocalDateTime alarmTime = LocalDateTime.parse(time, DateTimeFormatter.ISO_DATE_TIME);
System.out.println("闹钟设置为: " + alarmTime);
}
}
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
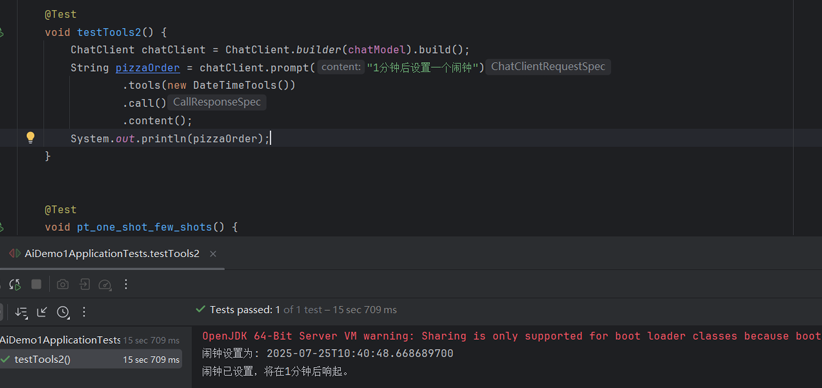
| @Test
void testTools2() {
ChatClient chatClient = ChatClient.builder(chatModel).build();
String pizzaOrder = chatClient.prompt("1分钟后设置一个闹钟")
.tools(new DateTimeTools())
.call()
.content();
System.out.println(pizzaOrder);
}
|
效果
3 工具定义方式
3.1 基于方法的工具
声明式定义(@Tool 注解)
注解参数:
- name:工具名称(默认方法名)。
- description:工具描述(关键,影响模型调用决策)。
- returnDirect:是否直接返回结果给客户端(默认 false,返回给模型)。
参数注解:
- @ToolParam(description = “参数说明”, required = false):设置参数描述和必填性。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
| public class Tools {
@Tool(description = "计算两数之和")
int add(@ToolParam(description = "第一个加数") int a, @ToolParam(description = "第二个加数") int b) {
System.out.println("add方法执行了...");
return a + b;
}
}
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
| @Test
void testTools2() {
ChatClient chatClient = ChatClient.builder(chatModel).build();
String content = chatClient.prompt("计算出100和1000两个数相加的结果")
.tools(new Tools())
.call()
.content();
System.out.println(content);
}
|
编程式定义
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
| public class Tools {
@Tool(description = "计算两数之和")
int add(@ToolParam(description = "第一个加数") int a, @ToolParam(description = "第二个加数") int b) {
System.out.println("add方法执行了...");
return a + b;
}
int add1( int a, int b) {
System.out.println("add1方法执行了...");
return a + b;
}
}
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
| @Test
void testTools3(){
Method method = ReflectionUtils.findMethod(Tools.class, "add1", int.class, int.class);
ToolCallback toolCallback = MethodToolCallback.builder()
.toolDefinition(ToolDefinition.builder(method)
.description("计算两数之和")
.build())
.toolMethod(method)
.toolObject(new Tools())
.build();
ChatClient chatClient = ChatClient.builder(chatModel).build();
String content = chatClient.prompt("计算出100和1000两个数相加的结果")
.toolCallbacks(toolCallback)
.call()
.content();
System.out.println(content);
}
|
3.2 基于函数的工具
编程式定义(FunctionToolCallback)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
|
interface WeatherService extends Function<WeatherRequest, WeatherResponse> {
@Override
WeatherResponse apply(WeatherRequest request);
}
record WeatherRequest(String location, DurationFormat.Unit unit) {}
record WeatherResponse(double temp, DurationFormat.Unit unit) {}
@Test
void testTools4(){
ToolCallback toolCallback = FunctionToolCallback.builder("currentWeather",new WeatherService(){
@Override
public WeatherResponse apply(WeatherRequest request) {
return new WeatherResponse(25.5,request.unit());
}
}).description("获取指定地点的天气")
.inputType(WeatherRequest.class)
.build();
ChatClient chatClient = ChatClient.builder(chatModel).build();
String content = chatClient.prompt("今天长沙的天气怎么样?")
.toolCallbacks(toolCallback)
.call()
.content();
System.out.println(content);
}
|
动态定义(@Bean 注解)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
| @Configuration
public class ToolConfig {
public static final String WEATHER_TOOL = "currentWeather";
@Bean(WEATHER_TOOL)
@Description("获取指定地点的天气")
Function<WeatherRequest, WeatherResponse> currentWeather() {
return request -> new WeatherResponse(30.0, request.unit());
}
}
record WeatherRequest(String location, DurationFormat.Unit unit) {}
record WeatherResponse(double temp, DurationFormat.Unit unit) {}
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
| @Test
void testTools5() throws Exception{
ChatClient chatClient = ChatClient.builder(chatModel).build();
String content = chatClient.prompt("今天长沙的天气怎么样?")
.toolNames(ToolConfig.WEATHER_TOOL)
.call()
.content();
System.out.println(content);
}
|
4 核心组件与接口
ToolCallback 接口:工具的核心接口,定义执行逻辑。
1
2
3
4
5
| public interface ToolCallback {
ToolDefinition getToolDefinition();
ToolMetadata getToolMetadata();
String call(String toolInput);
}
|
ToolDefinition 接口:工具元数据,供模型理解调用方式。
1
2
3
4
5
| public interface ToolDefinition {
String name();
String description();
String inputSchema();
}
|
ToolCallingManager:工具执行管理器,处理工具调用流程。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
|
@Bean
ToolCallingManager toolCallingManager() {
return ToolCallingManager.builder()
.exceptionProcessor(exception -> "工具调用失败: " + exception.getMessage())
.build();
}
|
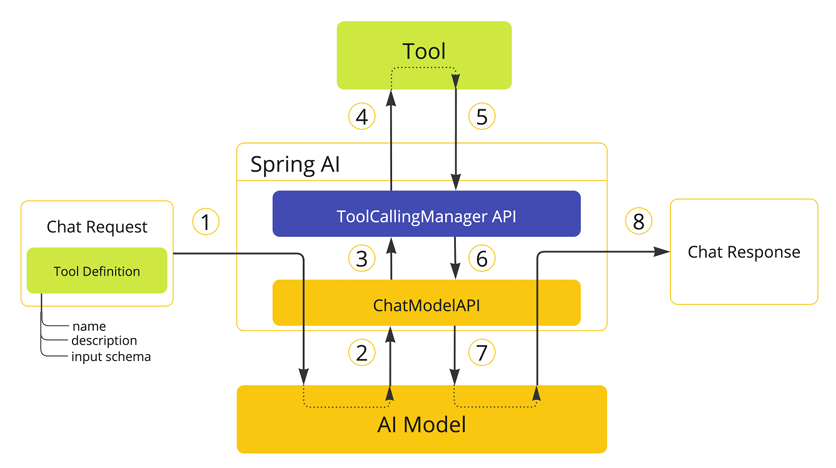
5 工具执行流程
框架控制执行(默认)
- 模型返回工具调用请求(含工具名和参数)。
- ChatModel 调用 ToolCallingManager 执行工具。
- 工具结果返回给模型,模型生成最终响应。
用户控制执行:手动处理工具调用循环。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
| @Test
void testTools6(){
ToolCallback toolCallback = FunctionToolCallback.builder("currentWeather",new WeatherService(){
@Override
public WeatherResponse apply(WeatherRequest request) {
return new WeatherResponse(25.5,request.unit());
}
}).description("获取指定地点的天气")
.inputType(WeatherRequest.class)
.build();
ChatOptions options = ToolCallingChatOptions.builder()
.toolCallbacks(toolCallback)
.internalToolExecutionEnabled(false)
.build();
Prompt prompt = new Prompt("北京今天的天气怎么样?适合做什么活动呢", options);
ChatResponse response = chatModel.call(prompt);
System.out.println(response.toString());
ToolCallingManager manager = ToolCallingManager.builder().build();
while (response.hasToolCalls()) {
ToolExecutionResult result = manager.executeToolCalls(prompt, response);
prompt = new Prompt(result.conversationHistory(), options);
response = chatModel.call(prompt);
System.out.println(response.getResult().getOutput().getText());
}
}
|
6 工具结果处理
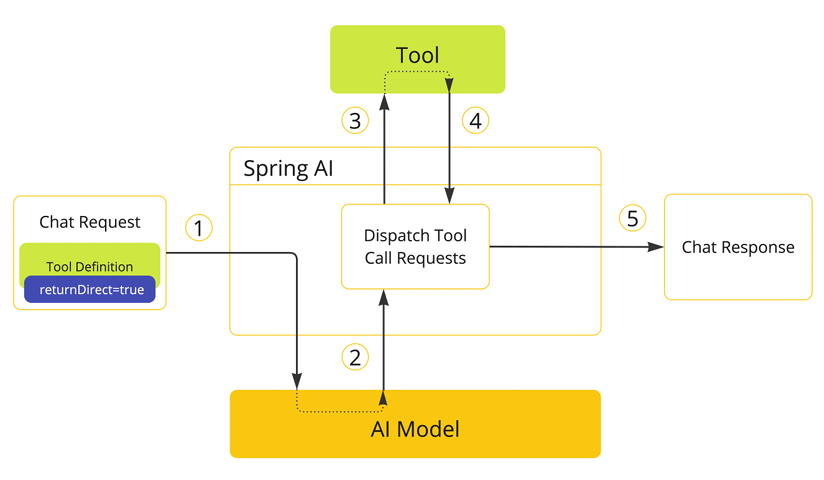
直接返回结果(returnDirect = true)
1
2
3
4
5
| @Tool(description = "获取用户信息", returnDirect = true)
UserInfo getUser(@ToolParam(description = "用户ID") Long id) {
return new UserInfo(id,"李四");
}
|
自定义结果转换
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
|
public class CustomConverter implements ToolCallResultConverter {
@Override
public String convert(Object result, Type returnType) {
if (result instanceof UserInfo) {
return "用户: " + ((UserInfo) result).getName();
}
return String.valueOf(result);
}
}
@Tool(description = "获取用户信息", returnDirect = true,resultConverter = CustomConverter.class)
UserInfo getUser(@ToolParam(description = "用户ID") Long id) {
return new UserInfo(id,"李四");
}
|
7 工具上下文与异常处理
工具上下文(ToolContext):传递额外参数(如租户 ID)。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
| ChatClient.create(chatModel)
.prompt("查询客户42的信息")
.tools(new CustomerTools())
.toolContext(Map.of("tenantId", "acme"))
.call().content();
@Tool(description = "查询客户信息")
Customer getCustomer(Long id, ToolContext context) {
String tenantId = context.get("tenantId");
return customerRepo.findByTenantAndId(tenantId, id);
}
|
异常处理:自定义工具执行异常处理器。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
| @Bean
ToolExecutionExceptionProcessor exceptionProcessor() {
return e -> {
if (e.getCause() instanceof SQLException) {
return "数据库错误: " + e.getMessage();
}
return "工具调用失败: " + e.getMessage();
};
}
|
8 工具与其他组件集成
与对话记忆(ChatMemory)集成:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
| ChatMemory memory = MessageWindowChatMemory.builder().build();
ChatClient client = ChatClient.builder(chatModel)
.defaultAdvisors(MessageChatMemoryAdvisor.builder(memory).build())
.defaultTools(new DateTimeTools())
.build();
String response = client.prompt("之前设置的闹钟时间是?").call().content();
|
与检索增强(RAG)集成:工具可调用向量存储检索上下文。
1
2
3
4
| @Tool(description = "检索相关文档")
List<Document> searchDocs(@ToolParam("查询关键词") String query) {
return vectorStore.search(query, 5);
}
|
9 支持的模型与最佳实践
支持模型:OpenAI、Anthropic Claude 3、Azure OpenAI、Mistral AI、Ollama 等。
最佳实践:
- 描述清晰:工具描述需明确用途和参数要求,避免模型误用。
- 参数必填性:合理设置 @ToolParam(required = false),防止模型虚构参数。
- 安全考虑:工具不应暴露敏感操作,结果直接返回时需验证权限。
- 性能优化:批量处理工具调用,减少模型交互次数。



