面向分布式、多语言异构化服务架构的流量治理组件
1 Sentinel入门小结

2 实时监控
实时监控仅存储 5 分钟以内的数据,如果需要持久化,需要通过调用实时监控接口来定制。
注意:请确保 Sentinel 控制台所在的机器时间与自己应用的机器时间保持一致,否则会导致拉不到实时的监控数据。
3 簇点链路
簇点链路(单机调用链路)页面实时的去拉取指定客户端资源的运行情况。它一共提供两种展示模式:一种用树状结构展示资源的调用链路,另外一种则不区分调用链路展示资源的运行情况。
注意:簇点监控是内存态的信息,它仅展示启动后调用过的资源
4 流控规则
资源名:相当于代码中的rule.setResource(“/user/hello”)->这个名称需要与Spring Web MVC端点的名称一致,只有这样限流时才能匹配得上
针对来源:可以根据不同的来源对/user/hello接口进行限流,比如针对来源a设置/user/hello的QPS为500,针对来源b设置/user/hello的QPS为1000
阈值类型:QPS or 并发线程数
单机阈值:比如设置阈值类型为QPS,单机阈值为2,则表示该资源/user/hello最大能接受每秒2个查询请求
是否集群:暂时先不关注
流控模式:直接、关联和链路
流控效果:快速失败、Warm Up和排队等待
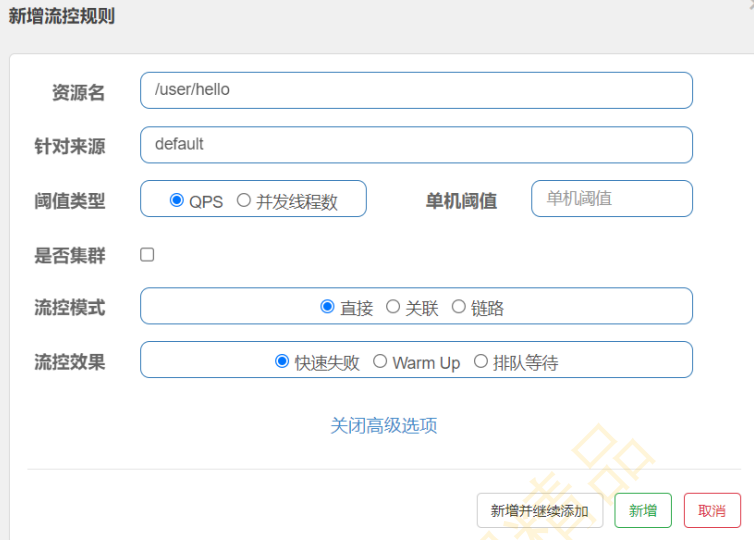
4.1 流控模式之直接
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
| 资源名:/user/hello
针对来源:default
阈值类型:QPS
单机阈值:2
是否集群:否
流控模式:直接
流控效果:快速失败
|
4.2 流控模式之关联
(1)在UserController中添加write和read两个api接口
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
| @RequestMapping("/write")
public String write(){
return "write ...";
}
@RequestMapping("/read")
public String read(){
return "read ...";
}
|
(2)重启Spring Boot项目,分别访问write和read接口,观察sentinel dashboard的展示
(3)理解关联模式业务场景:比如在高并发的场景下,如果修改用户信息的请求达到一定的阈值,则对读取用户的接口进行限流,相当于保护了修改用户的接口
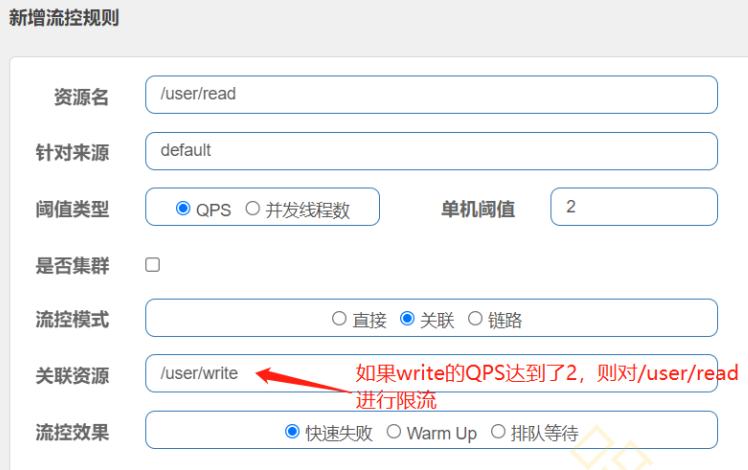
(4)写一段代码访问write接口,使其QPS阈值超过2,然后访问read接口,看是否有限流
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
| public class WriteQPS{
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
RestTemplate restTemplate = new RestTemplate();
for(int i = 0; i < 10000; i++){
String result = restTemplate.getForObject("http://localhost:8081/user/write", String.class);
System.out.printLn(result);
Thread.sleep(300);
}
}
}
|
(5)关联模式的使用条件 a. 两个资源具有竞争关系 b. 一个资源的优先级高,另外一个资源的优先级低
4.3 流控模式之链路
(1)创建OrderService,其中有一个query方法,并使用@SentinelResource注解保护起来
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
| @Service
public class OrderService{
@SentinelReesource(value = "orderQuery")
public String query(){
System.out.printLn("query orders....");
return "query orders....";
}
}
|
(2)创建OrderController,其实有两个接口,一个query一个update,并且这两个接口都需要调用 OrderService#query
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
| @RestController
@RequestMapping("/order")
public class OrderController{
@Resource
private OrderService orderService;
@RequestMapping("/query")
public String query() {
return "query: "+this.orderService.query();
}
@RequestMapping("/update")
public String update() {
System.out.println("do sth.");
return "update: "+this.orderService.query();
}
}
|
(3)重启Spring Boot项目,分别访问http://localhost:8081/order/query和http://localhost:8081/ord er/update,观察sentinel dashboard,发现update簇点链路下并没有显示orderQuery,这个问题先不管,直接进行配置
(4)链路模式
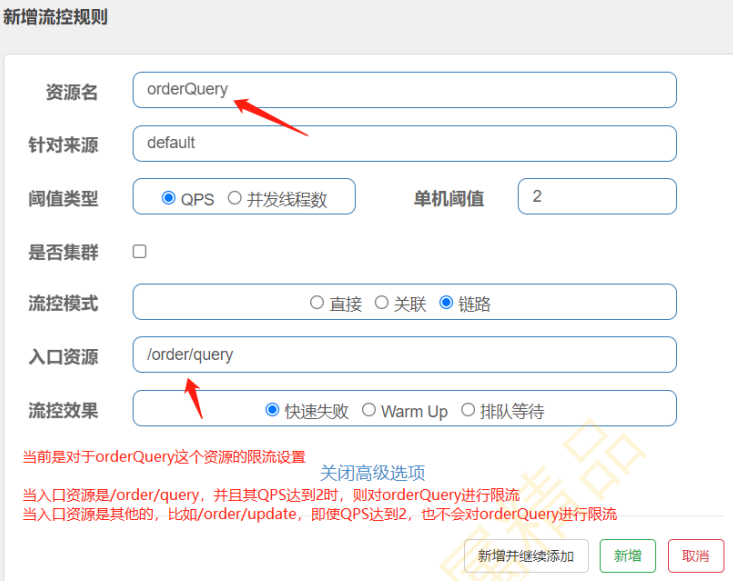
(5)配置好了之后,快速访问http://localhost:8081/order/query发现是不生效的,原因跟sentinel的 版本有关,具体可以参考https://github.com/alibaba/Sentinel/issues/1213进行解决
(6)如何解决?
添加sentinel-web-servlet依赖
1
2
3
4
| <dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba.csp</groupId>
<artifactId>sentinel-web-servlet</artifactId>
</dependency>
|
设置sentinel.filter.enable为false
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
| spring:
cloud:
sentinel:
transport:
dashboard: localhost:8080
filter:
enabled: false
|
新增Filter配置类,开放全部链路
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
| @Configuration
public class FilterCOnfiguration{
@Bean
public FilterRegistrationBean registrationBean(){
FilterRegistrationBean registrationBean = new FilterRegistrationBean();
registrationBean.setFilter(new CommonFilter());
registrationBean.addUrlPatterns("/*");
registrationBean.addInitParameter(CommonFilter.WEB_CONTEXT_UNIFY, "false");
registrationBean.setName("sentinelFilter");
return registrationBean;
}
}
|
重启Spring Boot项目,按照上述步骤进行重新测试
(7)流控异常如何处理?其实还是回到了@SentinelResource流控异常的处理
定义一个SentinelResource流控异常处理类
1
2
3
4
5
6
| public class SentinelResourceFlowExceptionHandler{
public static String handleBlock(BlockException e){
System.out.println("流控异常: "+e);
return "QPS超过阈值,流控了.";
}
}
|
修改orderService#query的异常处理
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
| @Service
public class OrderService {
@SentinelResource(value = "orderQuery",blockHandler = "handleBlock",blockHandlerClass = SentinelResourceFlowExceptionHandler.class)
public String query(){
System.out.println("query orders...");
return "query orders...";
}
}
|
5 流控效果
5.1 流控效果之快速失败
抛出异常
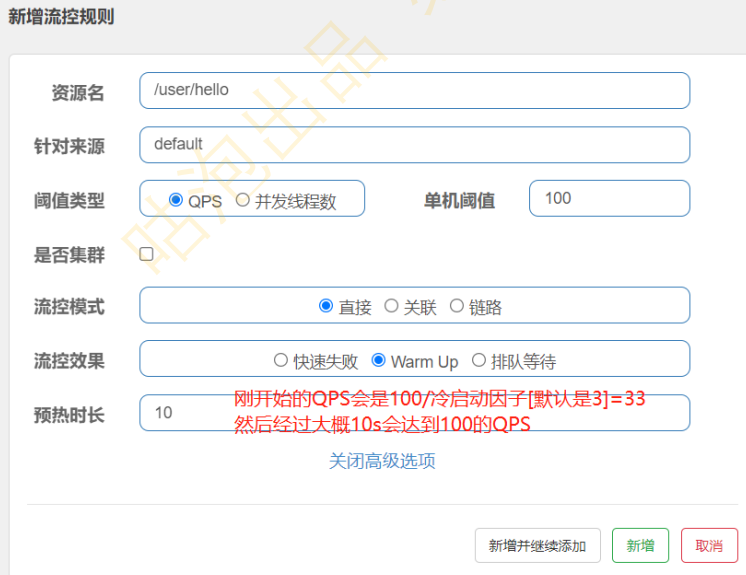
5.2 流控效果之Warm up
1
2
3
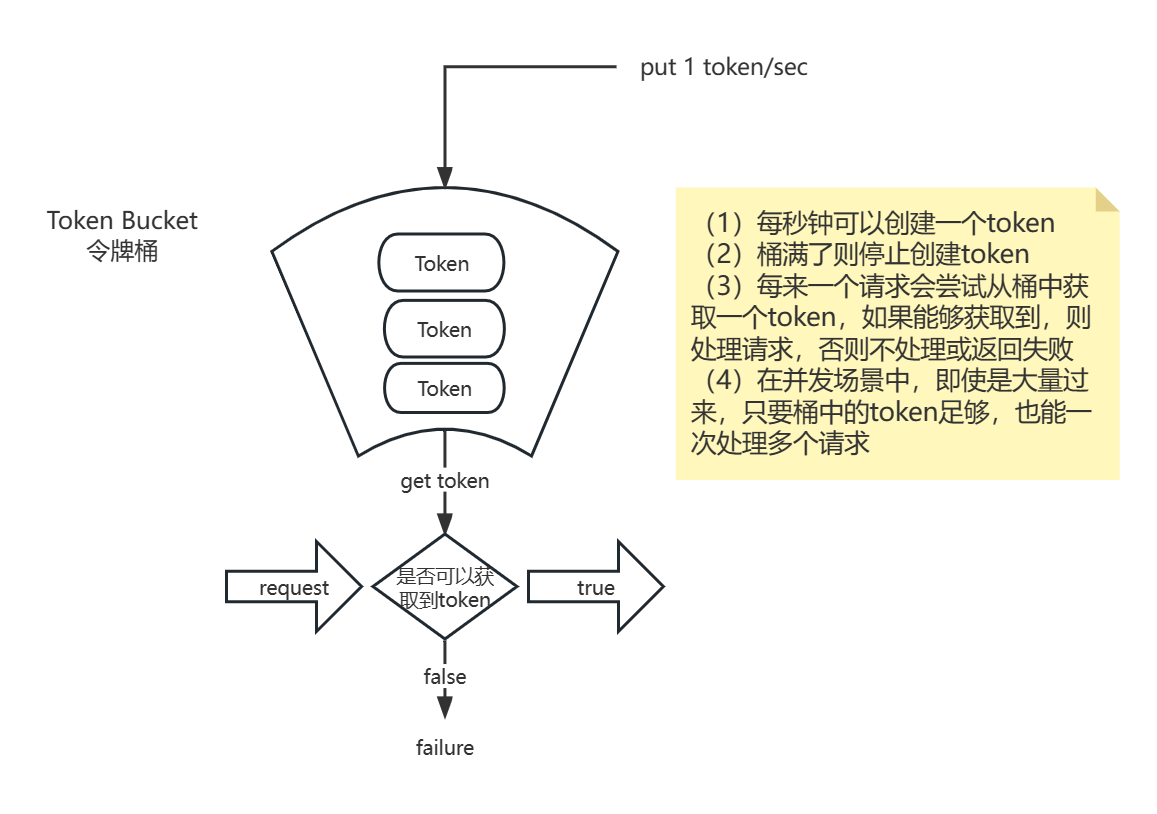
| 冷启动
基于令牌桶算法实现
适用于服务器刚启动或秒杀的场景
|
(1)令牌桶算法
(2)配置
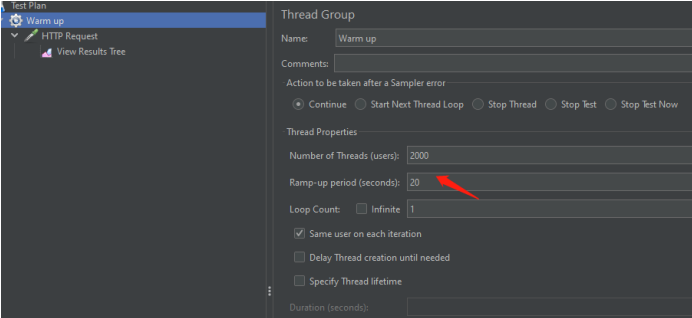
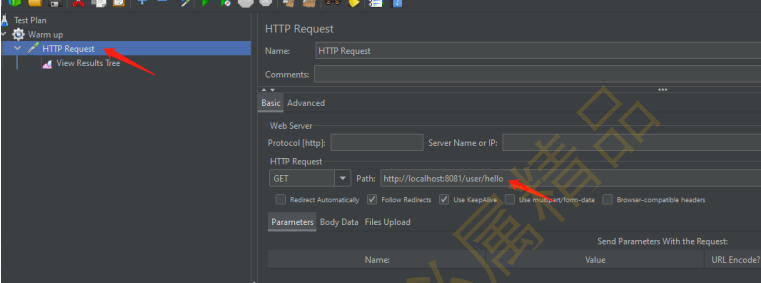
(3)jmeter配置
5.3 流控效果之排队等待
1
2
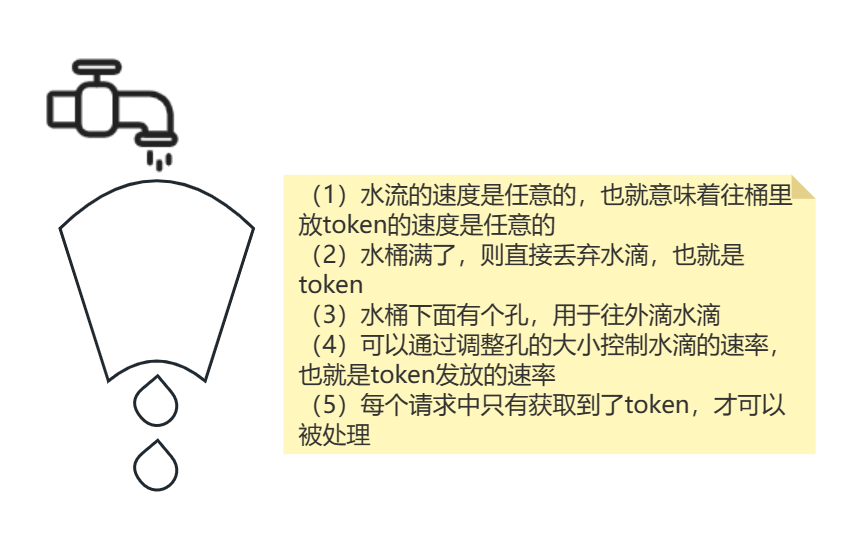
| 基于漏桶算法实现
可以用作流量整形:对于突发流量被整形以后能提供一个稳定的流量
|
(1)漏桶算法
(2)配置
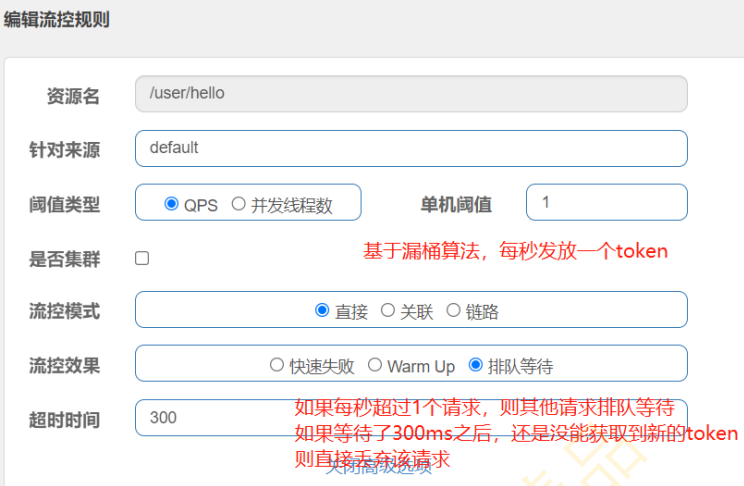
(3)代码与图解
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
| public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
RestTemplate restTemplate = new RestTemplate();
while (true){
String result = restTemplate.getForObject("http://localhost:8081/user/hello", String.class);
System.out.println(result);
Thread.sleep(500);
System.out.println("--------------");
}
}
|

(4)增加排队等待超时时长,比如将300ms修改成600ms,再次运行代码,发现调用正常

6 熔断规则
6.1 慢调用比例
(1)定义一个DegradeController类
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
| @RestController
@RequestMapping("/degrade")
public class DegradeController {
@RequestMapping("/hello")
public String hello() throws InterruptedException {
Thread.sleep(500);
return "hello sentinel degrade.";
}
}
|
(2)重启Spring Boot项目,访问http://localhost:8081/degrade/hello
(3)查看sentinel dashboard,可以看到该资源
(4)配置/degrade/hello的熔断规则
1
2
3
4
5
6
| 理解慢调用比例
在1s秒内,最少要有10个请求,如果有10*0.1=1个请求的请求响应时间超过100ms,断路器则从Closed变
成Open状态
10s之后,断路器从Open变成Half-Open状态,会放一个请求尝试调用一下
如果这个请求成功响应时间<100ms,则断路器从Half-Open变成Closed
如果这个请求成功响应时间>100ms,则断路器从Half-Open变成Open
|
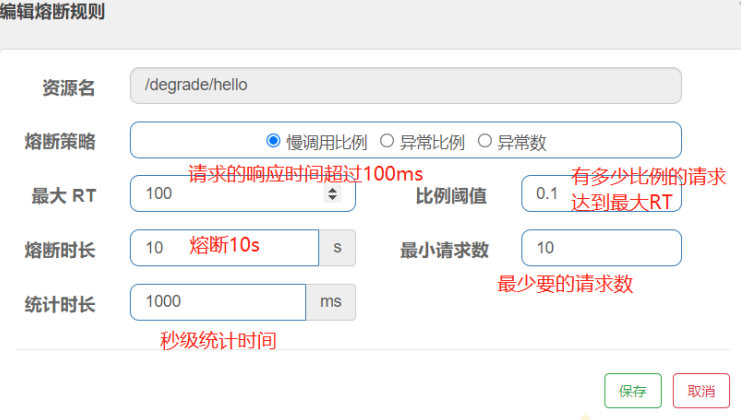
(5)使用jmeter进行测试
6.2 异常比例
理解异常比例:在1s之内,请求数量大于10,并且至少有1次请求有异常,接下来10s内会被熔断,10s之后,会尝试放 一个请求,若请求没有异常则断路器状态关闭,若请求有异常则断路器状态打开
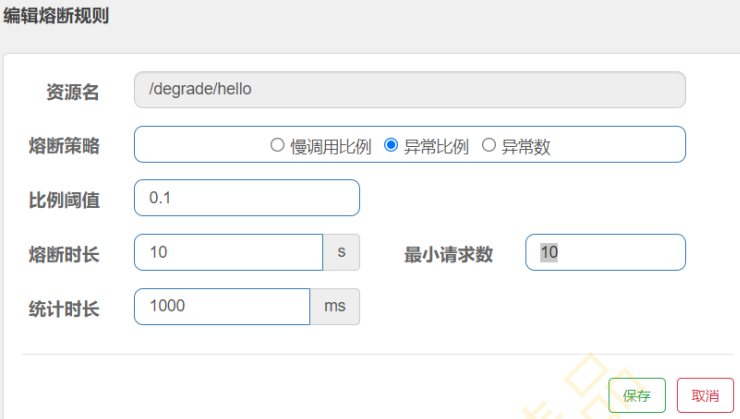
6.3 异常数
理解异常数: 在1s之内,请求数量大于10,并且至少有1次请求有异常,接下来10s内会被熔断,10s之后,会尝试放 一个请求,若请求没有异常则断路器状态关闭,若请求有异常则断路器状态打开
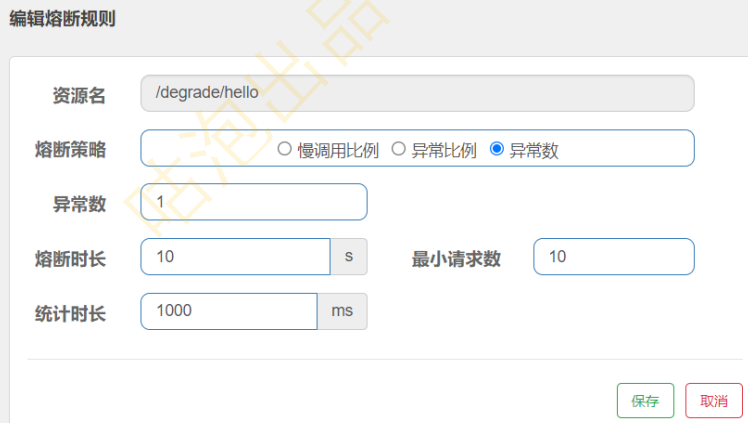
6.4 热点规则
(1)在FlowController中定义接口
1
2
3
4
5
| @RequestMapping("/say-hello")
public String sayHello(@RequestParam(value = "name",required = false) String name,
@RequestParam(value = "age",required = false) Integer age){
return "say hello : "+name+" age: "+age;
}
|
(2)访问http://localhost:8081/flow/say-hello?name=Jack&age=17,并设置热点规则
表示针对say-hello接口的第0个参数进行QPS为1的限流
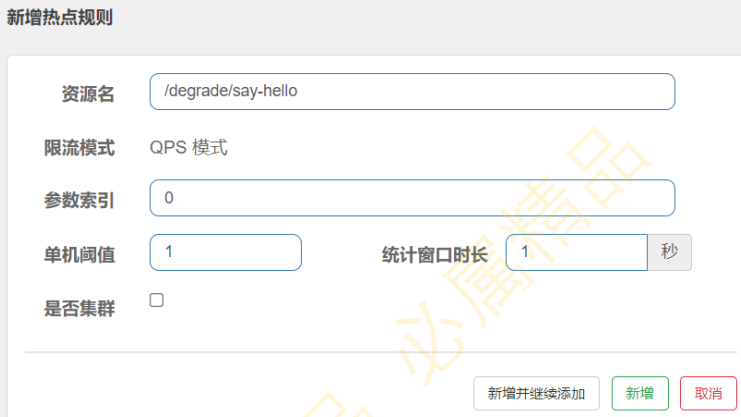
(3)访问:http://localhost:8081/degrade/say-hello?name=Jack,发现无效
(4)使用@SentinelResource注解
1
2
3
4
5
6
| @RequestMapping("/say-hello")
@SentinelResource("hot")
public String sayHello(@RequestParam(value = "name",required = false) String name,
@RequestParam(value = "age",required = false) Integer age){
return "say hello : "+name+" age: "+age;
}
|
(5)访问并设置热点规则
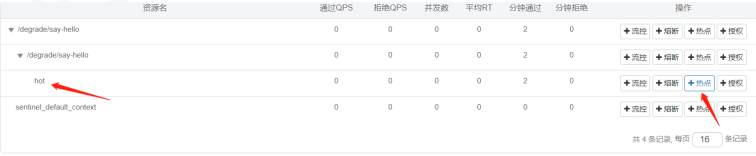
(6)分别访问如下接口进行测试
http://localhost:8081/degrade/say-hello?name=Jack
http://localhost:8081/degrade/say-hello?age=17
http://localhost:8081/degrade/say-hello?name=Jack&age=17
















